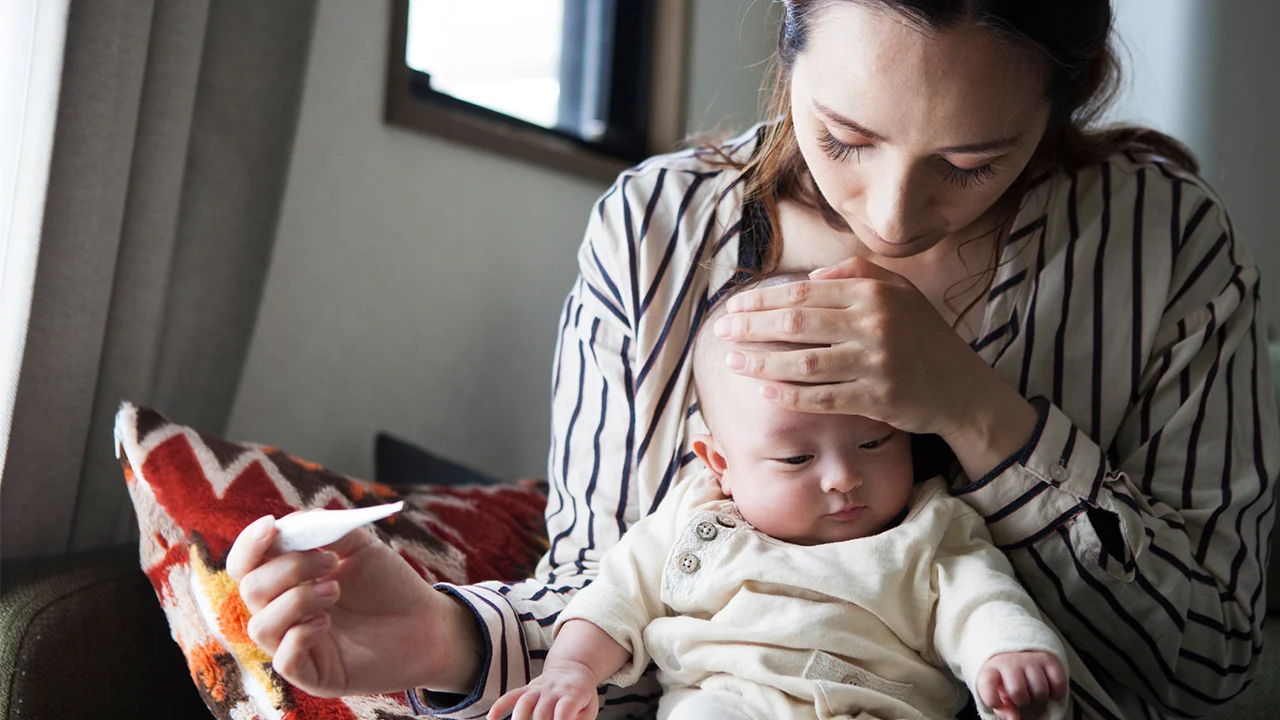
When your baby catches their first cold, it can be a nerve-wracking experience. Understanding what a cold is, its common causes, and why it’s important to recognize and manage your baby’s first cold can help alleviate some of the stress.
What is a Cold?
A cold is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, primarily affecting the nose and throat. It is typically caused by rhinoviruses but can also be triggered by other types of viruses. Colds are highly contagious and are spread through droplets from coughs and sneezes, or by touching contaminated surfaces.
Common Causes of Colds in Babies
Babies are particularly susceptible to colds due to their developing immune systems. Common causes include:
- Exposure to viruses from family members or caregivers
- Contact with contaminated surfaces (toys, doorknobs, etc.)
- Close interaction with other children in daycare or playgroups
Importance of Understanding Baby’s First Cold
Understanding your baby’s first cold helps you provide appropriate care, recognize when to seek medical attention, and prevent complications. It also prepares you to handle future illnesses more confidently.
Symptoms of Baby’s First Cold
Recognizing Early Signs
Early signs of a cold in babies can be subtle. Look for:
- Fussiness and irritability
- Decreased appetite
- Mild fever
- Sneezing and runny nose
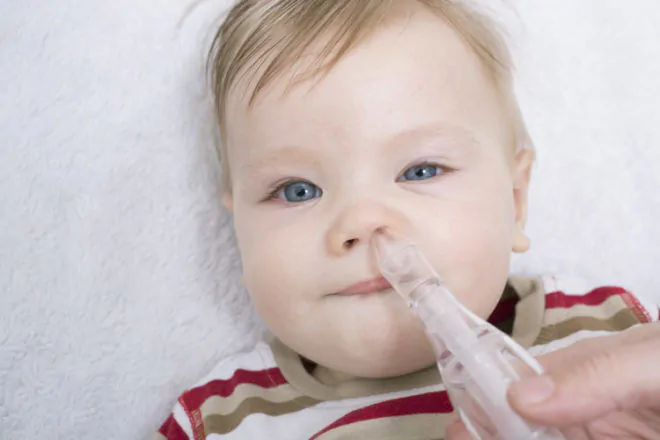

Common Symptoms
As the cold progresses, symptoms may include:
- Nasal congestion
- Coughing
- Sore throat
- Difficulty sleeping
- Watery eyes
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most colds are harmless, seek medical attention if your baby exhibits:
- High fever (above 100.4°F or 38°C) in infants under three months
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Persistent vomiting or diarrhea
- Signs of dehydration (dry mouth, fewer wet diapers)
- Unusual lethargy or irritability
Diagnosing a Cold in Babies
Pediatrician’s Role
Pediatricians play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing colds in babies. They will:
- Conduct a physical examination
- Assess symptoms and medical history
- Rule out other illnesses, such as flu or RSV
Home Diagnosis Tips
While home diagnosis is not a substitute for professional care, you can monitor your baby’s symptoms and comfort level. Keep track of:
- Temperature
- Frequency and severity of symptoms
- Changes in eating or sleeping patterns
Understanding the Difference Between a Cold and Other Illnesses
It’s important to differentiate between a common cold and more serious illnesses like the flu or respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Flu symptoms often include high fever and body aches, while RSV can cause severe respiratory distress in infants.
Immediate Steps to Take When Baby Has a Cold
Comforting Your Baby
Provide comfort through:
- Gentle rocking or holding
- Using a pacifier
- Playing soft, calming music
Maintaining Hydration
Keep your baby hydrated by:
- Offering breast milk or formula more frequently
- Giving small amounts of water (for babies over six months)
- Monitoring for signs of dehydration
Monitoring Fever
Use a digital thermometer to check your baby’s temperature. For fevers above 100.4°F (38°C), contact your pediatrician for advice on managing fever and ensuring your baby’s comfort.
Home Remedies for Baby’s Cold
Safe Home Remedies
Some safe home remedies include:
- Saline nasal drops and a bulb syringe to clear nasal congestion
- Elevating the head of the crib slightly to ease breathing
- Offering warm fluids like diluted apple juice (for babies over six months)
The Role of Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding can provide comfort and nutrients to help fight the cold. Breast milk contains antibodies that can strengthen your baby’s immune system.
Humidifiers and Their Benefits
Using a cool-mist humidifier can add moisture to the air, easing nasal congestion and coughing. Ensure regular cleaning to prevent mold and bacteria buildup.
Over-the-Counter Medications
What’s Safe for Babies
Always consult your pediatrician before giving any over-the-counter medications. Generally, avoid:
- Cough and cold medicines for babies under two years
- Aspirin (due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome)
Dosage and Administration
Follow your doctor’s guidance on safe medications and correct dosages. Use a medication syringe for accurate dosing and never give adult medications to babies.
Potential Side Effects
Be aware of potential side effects, such as drowsiness, stomach upset, or allergic reactions. Monitor your baby closely and report any adverse effects to your pediatrician.
Prescription Medications and Treatments
When Are They Needed?
Prescription medications may be necessary if your baby develops complications, such as a bacterial infection. Your pediatrician will determine if antibiotics or other treatments are required.
Common Prescriptions
Common prescriptions for complications might include:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Nebulizers or inhalers for severe respiratory issues
Safety and Effectiveness
Always follow the prescribed dosage and administration guidelines. Discuss any concerns or side effects with your pediatrician to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Natural Remedies and Alternatives
Herbal Teas and Natural Syrups
Consult your pediatrician before using any herbal teas or natural syrups. Some herbs may not be safe for infants, and it’s crucial to use age-appropriate remedies.
Aromatherapy for Babies
Aromatherapy can be used cautiously. Opt for baby-safe essential oils like lavender or chamomile, and use a diffuser to disperse the scent gently in the room.
Benefits and Risks
While natural remedies can provide relief, they also carry risks. Always research thoroughly and consult healthcare professionals to avoid potential hazards.
Preventing the Spread of the Cold
Hygiene Practices
Practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of the cold:
- Wash hands frequently
- Use hand sanitizer when soap and water are unavailable
- Clean and disinfect toys and surfaces regularly
Reducing Exposure to Germs
Limit your baby’s exposure to crowded places during cold seasons and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
Building Baby’s Immune System
Support your baby’s immune system through:
- A balanced diet (for babies on solids)
- Regular breastfeeding or formula feeding
- Ensuring adequate sleep and rest
Impact of Baby’s Cold on Sleep
Disrupted Sleep Patterns
Colds can disrupt your baby’s sleep patterns. To help them rest:
- Keep the sleeping area quiet and comfortable
- Use a humidifier to ease breathing
- Offer extra comfort and cuddles
Creating a Comfortable Sleep Environment
A comfortable sleep environment includes:
- A slightly elevated crib mattress
- Clean, dry bedding
- Proper room temperature
Napping Tips During Illness
Encourage napping by maintaining a consistent nap schedule and creating a calm, dark environment to promote restful sleep.
The Role of Nutrition in Recovery
Importance of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet supports recovery by providing essential nutrients. Offer a variety of fruits, vegetables, and proteins if your baby is on solids.
Foods That Boost Immunity
Foods that can boost immunity include:
- Breast milk or formula
- Pureed fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins A and C
- Hydrating fluids like water or diluted juices (for older babies)
Keeping Your Baby Well-Fed During a Cold
Ensure your baby is well-fed by offering smaller, more frequent feedings. Be patient and attentive to their hunger cues, as their appetite may vary.
When to Visit the Doctor
Signs That Require Medical Attention
Visit the doctor if your baby shows signs of:
- High fever (above 100.4°F or 38°C) lasting more than three days
- Difficulty breathing or persistent coughing
- Refusal to eat or drink
Preparing for the Doctor’s Visit
Prepare for the visit by:
- Keeping a record of symptoms and their duration
- Noting any medications or home remedies used
- Bringing a list of questions or concerns
What to Expect During the Appointment
During the appointment, the doctor will:
- Conduct a physical examination
- Possibly order tests to rule out other illnesses
- Provide guidance on treatment and care
Understanding Cold Complications
Secondary Infections
Secondary infections, such as ear infections or sinusitis, can occur. Watch for new or worsening symptoms and seek medical attention if needed.
Long-Term Health Effects
Most colds do not have long-term health effects, but repeated infections may indicate underlying health issues. Regular check-ups can help monitor your baby’s health.
Managing Complications
Manage complications by following your pediatrician’s advice and ensuring your baby completes any prescribed treatments.
Supporting Baby’s Comfort
Effective Soothing Techniques
Soothing techniques include:
- Gentle rocking or swaying
- Singing lullabies or playing soft music
- Offering a favorite blanket or toy
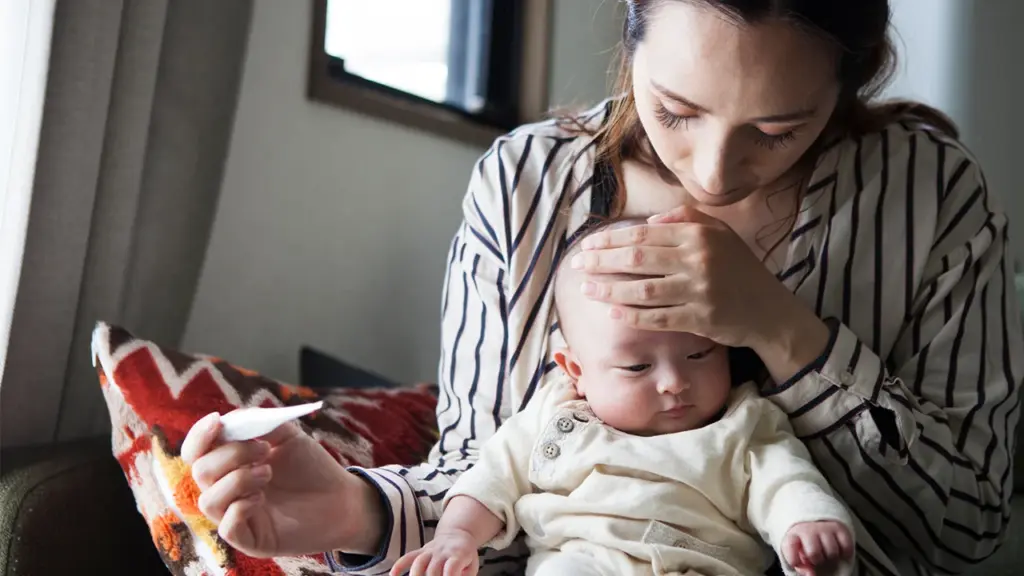

Importance of Cuddling and Skin-to-Skin Contact
Cuddling and skin-to-skin contact can provide comfort and security, helping your baby feel better during illness.
Creating a Calm Environment
Create a calm environment by:
- Keeping the room dimly lit
- Minimizing noise and distractions
- Ensuring a comfortable temperature
Tips for Caregivers
Self-Care for Parents and Caregivers
Caregivers should practice self-care by:
- Taking breaks when needed
- Ensuring adequate sleep and nutrition
- Seeking support from family and friends
Managing Stress and Anxiety
Manage stress and anxiety through:
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques
- Talking to a trusted friend or counselor
- Joining parenting support groups
Asking for Help
Don’t hesitate to ask for help from:
- Family members or friends
- Community resources
- Professional caregivers if needed
Differentiating Between Cold and Flu
Key Differences
Cold and flu have similar symptoms but differ in severity. Flu symptoms include high fever, body aches, and extreme fatigue.
Symptoms Comparison
Compare symptoms to differentiate:
- Cold: Mild fever, runny nose, mild cough
- Flu: High fever, severe body aches, fatigue, headache
Treatment Approaches
Treatments vary:
- Cold: Home remedies, hydration, rest
- Flu: Antiviral medications (if prescribed), rest, hydration
Vaccinations and Cold Prevention
Available Vaccines
While there is no vaccine for the common cold, vaccines for flu and other illnesses can prevent complications.
Importance of Vaccination
Vaccination helps protect against severe illnesses and reduces the spread of infections.
Myths and Facts
Educate yourself about vaccination myths and facts to make informed decisions for your baby’s health.
Role of Pediatricians and Healthcare Providers
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups ensure your baby’s overall health and help detect any issues early.
Trusted Advice and Resources
Pediatricians provide trusted advice and resources for managing colds and other health concerns.
Building a Relationship with Your Pediatrician
Build a strong relationship with your pediatrician for ongoing support and guidance.
Understanding Baby’s Immune System
How the Immune System Develops
A baby’s immune system develops gradually. Breastfeeding and vaccinations play key roles in strengthening immunity.
Role of Breastfeeding and Nutrition
Breastfeeding provides antibodies and essential nutrients, while a balanced diet supports overall health and immunity.
Strengthening Immunity
Strengthen immunity by:
- Ensuring proper nutrition
- Maintaining hygiene
- Providing a healthy environment
FAQs About Baby’s First Cold
Common Questions from Parents
Address common questions, such as:
- How long does a cold last in babies?
- Can I prevent my baby from catching a cold?
- What are safe remedies for a baby’s cold?
Expert Answers
Provide expert answers to reassure and guide parents through their concerns.
Additional Resources
Offer additional resources, such as:
- Pediatrician-approved websites
- Parenting books
- Support groups
Myths and Misconceptions About Baby Colds
Debunking Common Myths
Debunk myths, such as:
- Cold weather causes colds
- Antibiotics can treat colds
Evidence-Based Information
Share evidence-based information to help parents make informed decisions.
Educating Family and Friends
Educate family and friends about baby colds to ensure they provide accurate advice and support.
Preparing for Future Colds
Building a Cold-Preparedness Kit
Create a cold-preparedness kit with:
- Thermometer
- Saline drops and nasal aspirator
- Baby-safe fever reducers
Knowing When to Act
Know when to seek medical attention and when to use home remedies.
Long-Term Health Strategies
Adopt long-term health strategies, such as regular check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Psychological Impact on Parents
Dealing with Worry and Anxiety
Address parental worry and anxiety through:
- Open communication with healthcare providers
- Stress management techniques
- Seeking support
Finding Support Groups
Join support groups for shared experiences and advice.
Mental Health Resources
Access mental health resources for professional support.
Community Resources and Support
Local Health Resources
Utilize local health resources, such as clinics and health departments.
Online Support Communities
Join online communities for advice and emotional support.
How to Find Reliable Information
Learn how to find reliable health information online and offline.
Documenting Baby’s Health
Keeping a Health Diary
Maintain a health diary to track symptoms, treatments, and progress.
Monitoring Symptoms and Progress
Regularly monitor symptoms and progress to inform healthcare providers.
Sharing Information with Healthcare Providers
Share detailed information with healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Practical Tips for Everyday Care
Daily Hygiene Practices
Implement daily hygiene practices to prevent infections.
Creating a Safe Home Environment
Ensure your home environment is safe and clean.
Teaching Older Siblings
Teach older siblings about hygiene and how to prevent the spread of germs.
Traveling with a Sick Baby
Travel Preparations
Prepare for travel with a sick baby by packing essential items and planning rest stops.
Tips for Managing Symptoms on the Go
Manage symptoms on the go with:
- Hydration
- Comfort items
- Easy access to medications
When to Postpone Travel
Know when to postpone travel to ensure your baby’s health and safety.
Babysitting and Daycare Considerations
Communicating with Care Providers
Communicate with care providers about your baby’s cold and care needs.
Hygiene and Safety in Group Settings
Ensure hygiene and safety in group settings by:
- Providing hand sanitizer
- Keeping sick children home
Managing Sick Days
Manage sick days by planning backup care and maintaining communication with daycare providers.
Long-Term Health Monitoring
Regular Health Check-Ups
Schedule regular health check-ups to monitor your baby’s growth and development.
Identifying Patterns and Triggers
Identify patterns and triggers of illnesses to prevent future occurrences.
Ensuring Continued Wellness
Ensure continued wellness through:
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise (for older babies)
- Adequate sleep
Personal Stories and Experiences
Learning from Other Parents
Learn from other parents’ experiences with baby colds.
Sharing Your Journey
Share your journey to help and inspire other parents.
Inspirational Stories
Read inspirational stories to gain comfort and perspective.