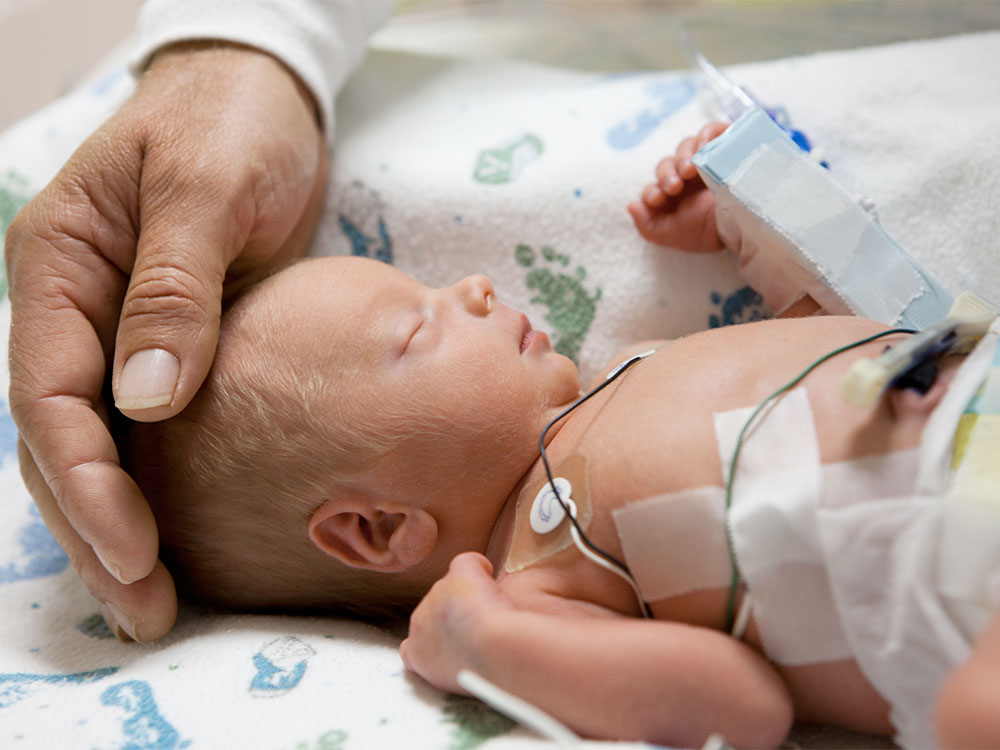
Premature birth presents unique challenges for both parents and healthcare providers. Understanding how to manage a preemie’s health effectively is crucial for ensuring their growth and development. This guide provides comprehensive tips and strategies to support parents in navigating the complexities of caring for a premature baby.
Understanding Prematurity
Definition and Causes of Prematurity
Prematurity refers to a baby born before 37 weeks of gestation. Causes can include multiple pregnancies, infections, chronic conditions, and complications during pregnancy. Understanding the underlying reasons for prematurity can help in managing and preventing future risks.
Common Health Challenges in Premature Babies
Premature babies often face health challenges such as respiratory issues, underdeveloped organs, feeding difficulties, and increased susceptibility to infections. Early identification and intervention are critical to address these issues effectively.
Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Early detection of health problems in preemies allows for timely medical interventions, which can significantly improve outcomes. Regular monitoring and medical check-ups are essential for identifying and addressing potential complications.
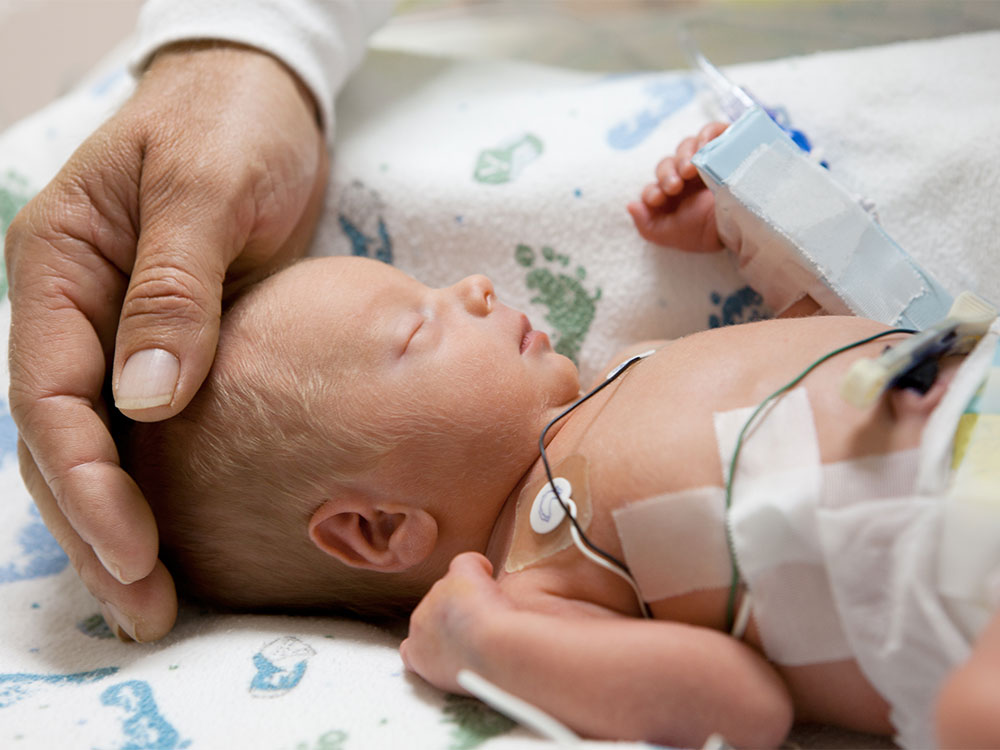
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) Essentials
What to Expect in the NICU
The NICU is a specialized unit equipped to care for premature and critically ill newborns. Understanding the NICU environment, including the equipment used and the roles of healthcare professionals, can help parents feel more comfortable and informed.
Understanding NICU Equipment and Procedures
Familiarize yourself with common NICU equipment such as incubators, ventilators, and feeding tubes. Understanding the purpose and function of these devices can alleviate anxiety and help you participate actively in your baby’s care.
Communicating with NICU Staff
Effective communication with NICU staff is crucial. Don’t hesitate to ask questions, express concerns, and seek clarification about your baby’s condition and treatment plan. Building a collaborative relationship with the healthcare team ensures the best care for your baby.
Feeding and Nutrition for Preemies
Breastfeeding and Pumping Tips
Breastfeeding a preemie can be challenging but is highly beneficial. Pumping breast milk and using specialized feeding techniques can help ensure your baby receives essential nutrients. Seek support from lactation consultants for guidance and assistance.
Supplemental Feeding Methods
In some cases, supplemental feeding methods such as tube feeding or fortifiers may be necessary to meet your baby’s nutritional needs. Work with healthcare providers to develop a feeding plan that supports your baby’s growth and development.
Monitoring Nutritional Intake and Growth
Regular monitoring of your baby’s weight, length, and head circumference is vital to assess their growth and nutritional status. Keep detailed records and communicate with your healthcare team to adjust feeding plans as needed.
Managing Respiratory Health
Understanding Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
RDS is a common condition in preemies due to immature lungs. Recognizing the signs and understanding the treatment options, such as surfactant therapy and respiratory support, can help manage this condition effectively.
Tips for Preventing Infections
Premature babies have a higher risk of infections due to their underdeveloped immune systems. Implement strict hygiene practices, limit exposure to sick individuals, and ensure proper vaccination to protect your baby.
Home Oxygen Therapy
Some preemies may require home oxygen therapy after discharge. Learn how to use and maintain oxygen equipment, monitor your baby’s oxygen levels, and recognize signs of respiratory distress to ensure safety and effective care.
Supporting Developmental Milestones
Tracking Developmental Progress
Regularly track your baby’s developmental milestones, such as motor skills, cognitive abilities, and social interactions. Use adjusted age to assess progress and seek early intervention if delays are noted.
Early Intervention Programs
Early intervention programs provide specialized support for preemies to promote development. These programs may include physical, occupational, and speech therapy tailored to your baby’s needs.
Encouraging Sensory Development
Engage your baby in sensory activities that stimulate their development. Use gentle touch, soothing sounds, and visual stimulation to enhance their sensory experiences and support overall growth.
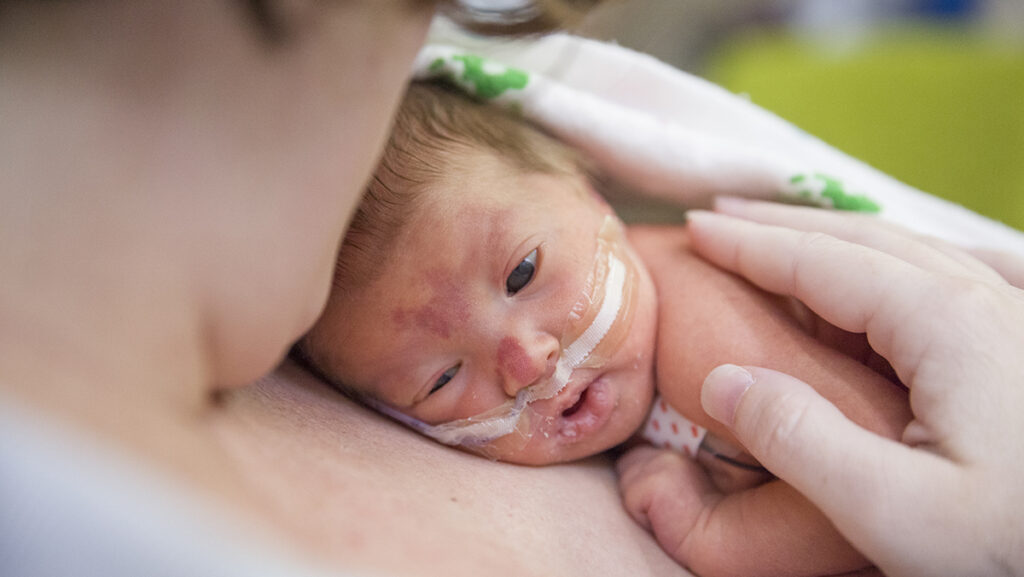
Emotional Support for Parents
Coping with Stress and Anxiety
Caring for a premature baby can be stressful and overwhelming. Practice stress management techniques, seek support from loved ones, and consider professional counseling to maintain your emotional well-being.
Building a Support Network
Connect with other parents of preemies through support groups and online communities. Sharing experiences and advice can provide comfort and practical tips for managing daily challenges.
Balancing Self-Care with Baby Care
Balancing self-care with baby care is crucial for your health and well-being. Take time for rest, engage in activities you enjoy, and ask for help when needed to ensure you can provide the best care for your baby.
Planning for Discharge and Home Care
Preparing Your Home for Your Preemie
Prepare your home for your preemie’s arrival by creating a safe and comfortable environment. Set up a nursery with necessary equipment, ensure proper hygiene, and establish a routine that supports your baby’s needs.
Coordinating Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential for monitoring your baby’s progress. Coordinate care with specialists, such as pediatricians and therapists, to ensure comprehensive support.
Developing a Care Plan
Develop a detailed care plan that includes feeding schedules, medication administration, and developmental activities. Share this plan with all caregivers to ensure consistency and continuity of care.
Long-Term Health and Development
Monitoring Long-Term Health Outcomes
Premature babies may face long-term health challenges. Regular monitoring of their health, development, and growth ensures that any issues are addressed promptly and appropriately.
Educational and Developmental Support
As your preemie grows, educational and developmental support becomes crucial. Work with educators and specialists to create individualized plans that support your child’s learning and development.
Preparing for School and Beyond
Preparing your preemie for school involves understanding their unique needs and ensuring they receive appropriate accommodations and support. Stay engaged with educators and advocate for your child’s rights to ensure a positive educational experience.