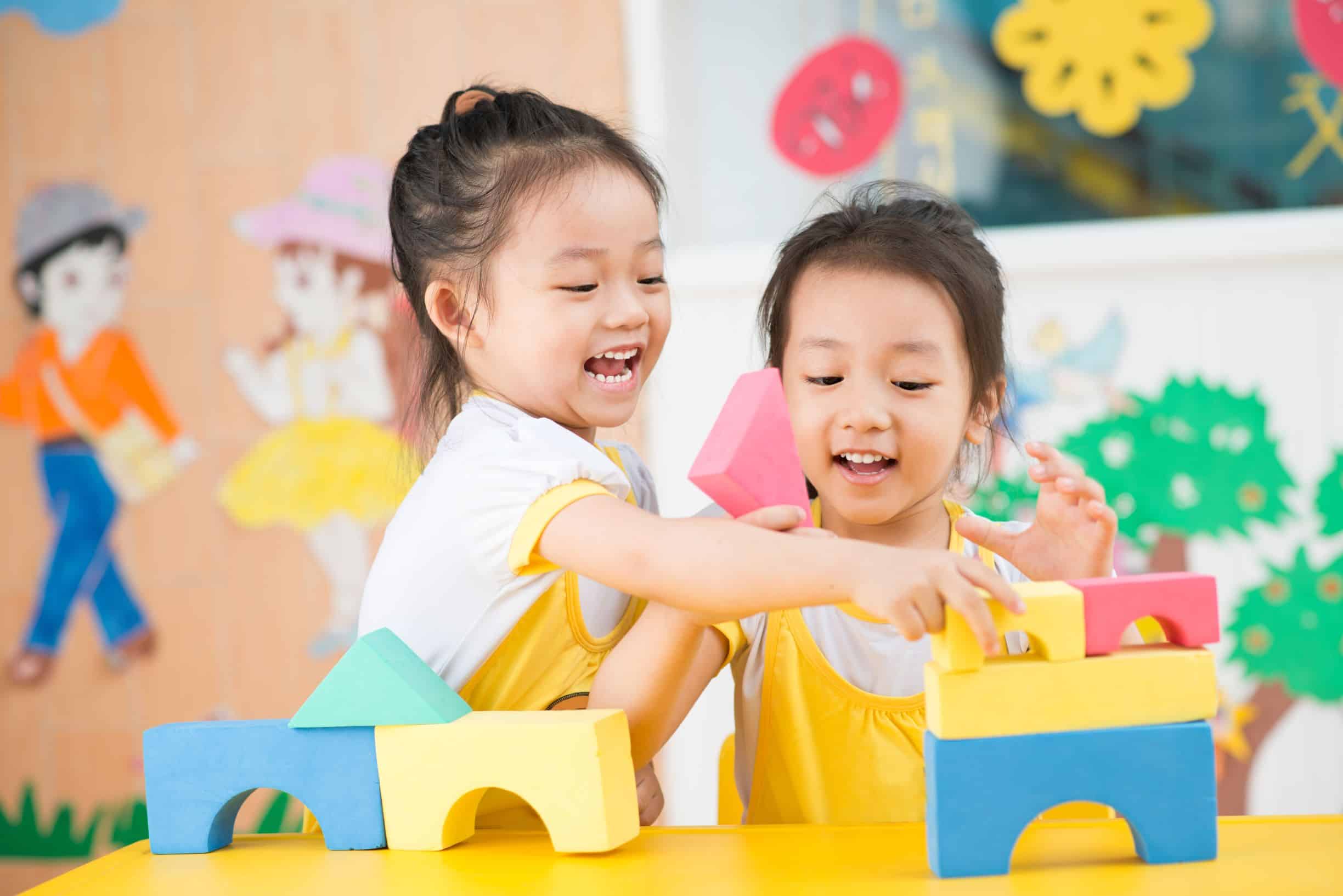
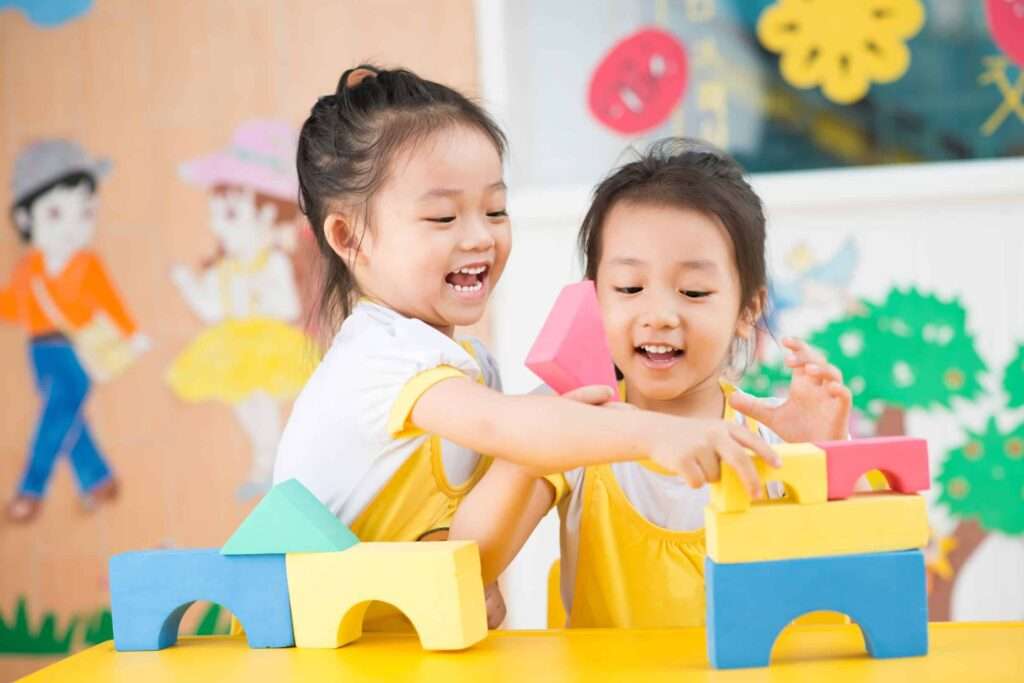
Play is an essential aspect of early childhood development, serving as a critical component in the growth and well-being of young children. It encompasses various activities that children engage in for enjoyment and recreation rather than for a serious or practical purpose. The importance of play in early childhood development cannot be overstated, as it plays a significant role in physical, cognitive, emotional, and social development.
Early childhood development refers to the process through which young children grow and develop their physical, cognitive, emotional, and social skills. This period, which typically spans from birth to eight years old, is crucial for laying the foundation for lifelong learning and development. Play, in its many forms, is a natural and vital part of this process, offering numerous benefits that contribute to a child’s overall development.
Types of Play
Physical Play
Physical play involves activities that require bodily movement and physical exertion. This type of play helps children develop motor skills, improve physical health, and enhance coordination and balance. Activities such as running, jumping, climbing, and dancing fall under this category.
Social Play
Social play involves interactions with peers or adults, helping children develop social skills such as cooperation, sharing, and communication. This type of play includes activities like playing house, role-playing, and group games.
Constructive Play
Constructive play involves creating or building something, often with materials like blocks, sand, or art supplies. This type of play helps children develop problem-solving skills, fine motor skills, and creativity.
Fantasy Play
Fantasy play, also known as pretend play, involves children using their imagination to create scenarios and roles. This type of play encourages creativity, language development, and emotional understanding.
Games with Rules
Games with rules involve structured activities that require children to follow guidelines and cooperate with others. Examples include board games, sports, and card games. These activities help children understand the importance of rules, fairness, and teamwork.

Physical Benefits of Play
Development of Motor Skills
Physical play is crucial for the development of both gross and fine motor skills. Activities such as running, jumping, and climbing help strengthen large muscle groups, while tasks like drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects enhance fine motor skills. These skills are foundational for many daily activities and academic tasks.
Enhancing Physical Health
Engaging in regular physical play promotes overall physical health. It helps children maintain a healthy weight, improves cardiovascular health, and strengthens bones and muscles. Active play also reduces the risk of childhood obesity and related health issues.
Promoting Coordination and Balance
Physical play activities require children to use their bodies in coordinated ways, which enhances their balance and spatial awareness. Activities like balancing on beams, hopping on one foot, and navigating obstacle courses help develop these essential skills.
Cognitive Benefits of Play
Stimulating Brain Development
Play stimulates brain development by encouraging neural connections and enhancing brain function. Engaging in various play activities helps children develop cognitive skills such as memory, attention, and executive function, which are crucial for learning and problem-solving.
Enhancing Problem-Solving Skills
Through play, children encounter and solve various problems, from figuring out how to build a stable tower with blocks to navigating social interactions in a group game. These experiences help develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills that are valuable throughout life.
Encouraging Creativity and Imagination
Play, particularly fantasy play, allows children to use their imagination and creativity. By creating and exploring new scenarios, children learn to think creatively, which enhances their ability to come up with innovative solutions to problems.
Emotional Benefits of Play
Building Self-Esteem and Confidence
Successful play experiences help children build self-esteem and confidence. When children achieve goals during play, such as building a tall block tower or successfully navigating a social interaction, they feel a sense of accomplishment that boosts their self-confidence.
Managing Stress and Anxiety
Play provides an outlet for children to express and manage their emotions. Engaging in play allows children to release pent-up energy and stress, helping them feel more relaxed and less anxious. It also provides opportunities for children to work through difficult emotions in a safe and supportive environment.
Understanding and Expressing Emotions
Through play, children learn to understand and express their emotions. Role-playing and pretend play allow children to explore different emotional responses and develop empathy for others. This emotional understanding is critical for social development and emotional regulation.
Social Benefits of Play
Learning Cooperation and Sharing
Social play requires children to interact with others, which helps them learn important social skills such as cooperation, sharing, and taking turns. These skills are essential for building positive relationships and functioning effectively in group settings.
Developing Communication Skills
Play provides numerous opportunities for children to develop and practice communication skills. Whether negotiating roles in a pretend game or explaining the rules of a game, children learn to express themselves clearly and listen to others.
Building Friendships and Relationships
Play is a natural way for children to build friendships and relationships. Shared play experiences create bonds between children and provide a foundation for lasting friendships. These relationships are important for social and emotional development.
Play and Language Development
Enhancing Vocabulary and Language Skills
Through play, children are exposed to new vocabulary and language structures. Engaging in pretend play and storytelling helps children expand their vocabulary and improve their language skills, which are critical for literacy development.
Promoting Narrative Skills
Play, particularly pretend play, encourages children to create and tell stories. This helps develop narrative skills, which are important for reading comprehension and writing. Children learn to organize their thoughts and express them in a coherent and logical manner.
Encouraging Listening and Understanding
Play requires children to listen to others and understand their perspectives. This helps develop listening skills and the ability to understand and interpret spoken language. These skills are essential for effective communication and academic success.
Play in Different Early Childhood Settings
Play at Home
Home is often the first place where children engage in play. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in providing a safe and stimulating environment for play. Simple activities such as playing with toys, reading books, and engaging in outdoor play can have significant benefits for early childhood development.
Play in Preschool
Preschools provide structured play opportunities that support various aspects of development. Play-based learning is an integral part of the preschool curriculum, helping children develop cognitive, social, and emotional skills in a supportive environment.
Play in Daycare
Daycare centers offer opportunities for children to engage in both structured and unstructured play. Caregivers facilitate play activities that promote development and provide a safe space for children to explore and interact with peers.
Play in Outdoor Environments
Outdoor play provides unique benefits for early childhood development. Nature offers a stimulating environment that encourages exploration and physical activity. Activities such as playing in the park, exploring nature trails, and engaging in outdoor games promote physical health and cognitive development.

The Role of Adults in Facilitating Play
Parents’ Role in Encouraging Play
Parents play a vital role in encouraging play by providing time, space, and resources for play activities. They can engage in play with their children, provide a variety of play materials, and create a safe and supportive environment for play.
Teachers’ Role in Structured Play
Teachers facilitate structured play activities that promote learning and development. By incorporating play-based learning into the curriculum, teachers help children develop essential skills in a fun and engaging way. They also provide guidance and support to help children navigate social interactions during play.
Caregivers’ Role in Supervised Play
Caregivers, such as daycare providers and nannies, play an important role in supervising play to ensure safety and promote development. They can create opportunities for play, provide appropriate materials, and guide children in their play activities.